Buzzer
The piezo buzzer produces sound based
on reverse of the piezoelectric effect. The generation of pressure variation or
strain by the application of electric potential across a piezoelectric material
is the underlying principle. These buzzers can be used alert a user of an event corresponding
to a switching action, counter signal or sensor input. They are also used in
alarm circuits.
The buzzer produces a same noisy sound
irrespective of the voltage variation applied to it. It consists of piezo
crystals between two conductors. When a potential is applied across these
crystals, they push on one conductor and pull on the other. This, push and pull
action, results in a sound wave. Most buzzers produce sound in the range of 2
to 4 kHz.
The
Red lead is connected to the Input and the Black lead is connected to Ground
Buzzer is an electrical device, which is similar to a bell
that makes a buzzing noise and is used for signaling. Typical uses of buzzers
and beepers include alarm devices, timers and confirmation of user input such
as a mouse click or keystroke.
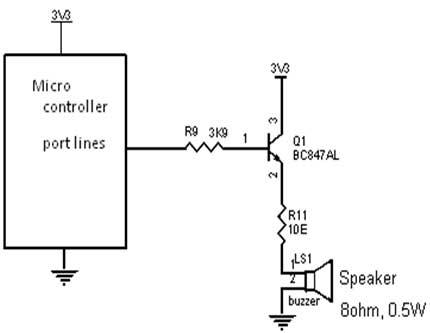
Interfacing Buzzer
Fig. 1 shows how to interface the Buzzer to microcontroller.
A piezoelectric element may be driven by an oscillating electronic circuit or
other audio signal source, driven with a piezoelectric audio amplifier. Sounds
commonly used to indicate that a button has been pressed are a click, a ring or
a beep. When the input port pin from microcontroller is changed, the sound wave
is changed in Buzzer.
Fig. 1 Interfacing
Buzzer to Microcontroller

No comments:
Post a Comment